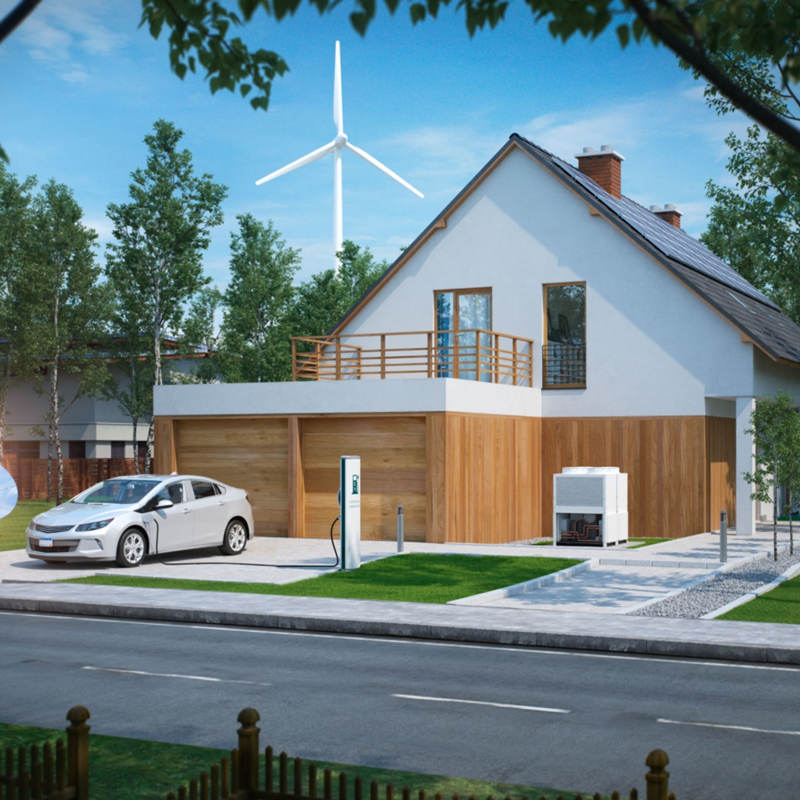
What is Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)?
Vehicle-to-home (V2H) is a technology that allows electric vehicles (EVs) to power homes and businesses. It works by using the battery in an EV to store energy from the grid or from renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. This energy can then be used to power the home or business when needed, such as during a power outage or when electricity prices are high.
How V2H works
V2H technology uses a bidirectional charger to transfer energy between the EV battery and the home or business. This charger allows the EV to both charge and discharge its battery.
To charge the EV battery, the charger draws electricity from the grid. To power the home or business, the charger sends electricity from the EV battery to the home or business electrical panel.
Benefits of V2H
V2H offers a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced energy costs: V2H can help to reduce energy costs by allowing homeowners and businesses to store energy when electricity prices are low and use it when prices are high.
- Increased energy resilience: V2H can help to increase energy resilience by providing a backup power source during power outages.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: V2H can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by promoting the use of renewable energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Drawbacks of V2H
Vehicle-to-home (V2H) is a promising technology with the potential to revolutionize the way we use and manage energy. However, there are still some drawbacks to V2H technology that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted.
Cost
One of the biggest drawbacks of V2H is the cost of the systems. Bidirectional chargers, which are required for V2H, can be expensive to purchase and install. Additionally, V2H systems may require additional electrical equipment, such as a smart meter or a home energy management system (HEMS), which can also increase costs.
Complexity
V2H systems can be complex to set up and operate. This is because V2H systems involve the interaction of multiple energy systems, including the EV battery, the home or business electrical panel, and the grid. Additionally, V2H systems may require users to understand complex energy concepts, such as time-of-use electricity rates and demand response programs.
Limited availability
V2H technology is still new, so it is not yet widely available. There are a limited number of bidirectional chargers on the market, and V2H systems may not be compatible with all EVs. Additionally, some areas may have regulations that prevent homeowners and businesses from using V2H technology.
Reduced EV range
Using the EV battery to power the home or business can reduce the EV’s range.
Battery degradation
Repeatedly charging and discharging the EV battery can accelerate battery degradation.
Safety risks
V2H systems can pose safety risks if they are not installed and used properly.
Despite these drawbacks, V2H technology has the potential to offer a number of benefits, such as reduced energy costs, increased energy resilience, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
As V2H technology continues to develop and become more affordable and accessible, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in the energy grid.
How to address the drawbacks of V2H
The following are some ways to address the drawbacks of V2H technology:
Reduce costs: Governments and utilities can offer subsidies and incentives to help homeowners and businesses purchase and install V2H systems. Additionally, the cost of V2H systems is expected to decrease as the technology becomes more widely adopted.
Simplify V2H systems: V2H system manufacturers can make V2H systems easier to set up and operate by developing more user-friendly interfaces and providing better documentation.
Additionally, utilities and other organizations can offer educational programs to help homeowners and businesses learn about V2H technology.
Increase V2H availability: V2H system manufacturers can increase the availability of V2H systems by increasing production and expanding their distribution networks.
Additionally, governments can work to remove regulatory barriers to V2H implementation.
Address other drawbacks: V2H system manufacturers can address other drawbacks, such as reduced EV range and battery degradation, by developing new technologies that improve the efficiency of V2H systems and reduce the impact on the EV battery.
Additionally, homeowners and businesses can take steps to mitigate these drawbacks, such as using the EV battery to power the home or business during off-peak hours and avoiding overcharging the EV battery.
By addressing the drawbacks of V2H technology, we can accelerate the adoption of this promising technology and reap its many benefits.
Types of Vehicle-to-Home Systems
There are two main types of V2H systems:
Uni-directional V2H systems: Uni-directional V2H systems only allow the EV battery to power the home or business. They cannot charge the EV battery from the home or business.
Bi-directional V2H systems: Bi-directional V2H systems allow the EV battery to both power and charge from the home or business.
V2H Applications
V2H technology can be used for a variety of applications, including:
Powering homes during power outages: V2H can be used to power homes during power outages, providing a backup power source for essential appliances and devices.
Reducing energy costs: V2H can help to reduce energy costs by allowing homeowners to store energy when electricity prices are low and use it when prices are high.
Providing energy storage for utilities: V2H can provide energy storage for utilities, helping them to manage the grid and meet demand during peak periods.
Supporting the integration of renewable energy into the grid: V2H can help to support the integration of renewable energy into the grid by providing a way to store excess renewable energy and use it when needed.
How to Implement V2H Technology
To implement V2H technology, you will need to purchase and install a bidirectional charger. You will also need to have a compatible EV.
Once you have installed the bidirectional charger, you will need to set it up to work with your EV and your home or business electrical panel.
You may also need to install additional electrical equipment, such as a smart meter or a home energy management system (HEMS).
The Future of Vehicle-to-Home
V2H technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we use and manage energy. As EVs become more common and V2H technology becomes more affordable and accessible, V2H is expected to play an increasingly important role in the energy grid.
Challenges to V2H Implementation
One of the biggest challenges to V2H implementation is the cost of V2H systems. Bidirectional chargers can be expensive to purchase and install.
Another challenge is the lack of standardization in V2H technology. There is currently no single standard for V2H systems, which can make it difficult to choose and install the right system for your needs.
Finally, there are some regulatory barriers to V2H implementation. In some areas, there are regulations that prevent homeowners and businesses from using V2H technology.
Trends and Developments in Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) Technology
The V2H technology market is growing rapidly, and there are a number of trends and developments that are driving this growth.
One trend is the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs).
As EVs become more common, there is a growing demand for V2H technology. V2H systems allow EV owners to use their EV batteries to power their homes and businesses, which can save them money on their energy bills and increase their energy resilience.
Another trend is the declining cost of V2H systems.
Bidirectional chargers, which are required for V2H, have become more affordable in recent years. Additionally, the cost of other V2H equipment, such as smart meters and HEMS, has also decreased.
Another trend is the development of new V2H technologies.
V2H system manufacturers are developing new technologies to improve the efficiency and functionality of V2H systems.
For example, some manufacturers are developing V2H systems that can automatically optimize energy use based on real-time electricity prices and grid conditions.
Finally, there is a growing interest in V2H from utilities and other organizations.
Utilities are interested in V2H because it can help them to manage the grid more efficiently and meet demand during peak periods. Other organizations, such as government agencies and businesses, are also interested in V2H because it can help them to reduce their energy costs and increase their energy resilience.
Here are some specific examples of trends and developments in V2H technology:
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration: V2G technology allows V2H systems to interact with the grid. This allows EV owners to sell electricity back to the grid when prices are high or when there is a surplus of renewable energy.
Smart V2H systems: Smart V2H systems use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to optimize energy use. For example, smart V2H systems can learn about the homeowner’s energy consumption patterns and electricity prices to automatically schedule charging and discharging of the EV battery.
Wireless V2H charging: Wireless V2H charging systems eliminate the need for cables, making V2H systems more convenient and user-friendly.
V2H systems for commercial and industrial applications: V2H systems are not just for homes. V2H systems can also be used in commercial and industrial applications to reduce energy costs and increase energy resilience.
The Future of Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) Technology
V2H technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we use and manage energy. As EVs become more common, V2H technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in the energy grid.
V2H technology can help to:
- Reduce energy costs for homeowners and businesses
- Increase energy resilience during power outages
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by supporting the integration of renewable energy into the grid
- Help utilities to manage the grid more efficiently and meet demand during peak periods
As V2H technology continues to develop and become more affordable and accessible, it is expected to be widely adopted in both residential and commercial applications.
Which Industries Benefit from Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)?
V2H technology has the potential to benefit a wide range of industries, including the automotive industry, the energy industry, utilities, and technology companies. V2H technology can help to make EVs more affordable and practical for consumers, make the energy grid more efficient and resilient, help utilities to reduce costs and improve customer service, and create new opportunities for technology companies.
As V2H technology continues to develop and become more affordable and accessible, it is expected to be widely adopted in a variety of industries.
V2H technology has the potential to benefit a wide range of industries, including:
Automotive industry: V2H technology could help to increase the adoption of EVs by making them more affordable and practical for consumers. For example, V2H systems could allow EV owners to use their EV batteries to power their homes during peak hours, which could save them money on their electricity bills.
V2H systems could also allow EV owners to sell electricity back to the grid, which could generate additional revenue.
Energy industry: V2H technology could help to make the energy grid more efficient and resilient. For example, V2H systems could help to reduce demand on the grid during peak hours and provide backup power during power outages.
V2H systems could also help to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid by storing excess renewable energy when it is generated and using it when it is needed.
Utilities: V2H technology could help utilities to reduce costs and improve customer service. For example, V2H systems could help utilities to reduce the need to build new power plants and transmission lines.
V2H systems could also help utilities to manage the grid more efficiently and reduce the risk of power outages.
Technology companies: V2H technology is a rapidly developing field, which presents opportunities for technology companies to develop new products and services.
For example, technology companies could develop new V2H systems, new software to manage V2H systems, and new services to help consumers and businesses use V2H technology.
Here are some specific examples of how V2H technology is being used in these industries today:
Automotive industry: Nissan and General Motors are both developing V2H systems for their EVs. Nissan’s V2H system is called the Leaf to Home system, and it allows Nissan Leaf owners to use their EV batteries to power their homes during power outages. General Motors’ V2H system is called the V2X system, and it is still under development.
Energy industry: The California Energy Commission is funding a pilot project to test the use of V2H systems to provide energy storage for the grid. The project is called the Vehicle-Grid Integration Pilot, and it is being led by Pacific Gas & Electric.
Utilities: The utility company Hawaiian Electric is offering a V2H program to its customers. The program allows customers to earn credits on their electricity bills for using their EV batteries to power their homes during peak hours.
Technology companies: The technology company Sunrun is developing a V2H system that is integrated with its solar energy products. The system, called the Sunrun Home Energy Management System, allows Sunrun customers to use their EV batteries to store excess solar energy and use it when it is needed.
V2H technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we generate, store, and use energy. As V2H technology becomes more affordable and accessible, it is expected to be widely adopted in a variety of industries.
How to Choose the Right V2H System for Your Needs
Vehicle-to-home (V2H) technology allows you to use your electric vehicle (EV) battery to power your home or business. V2H systems can be used to reduce energy costs, increase energy resilience, and support the integration of renewable energy into the grid.
When choosing a V2H system, there are a few things to consider:
1. The type of EV you have
Not all EVs are compatible with V2H systems. Make sure to choose a V2H system that is compatible with the make and model of your EV.
2. Your energy needs
Consider how much energy you need your V2H system to provide. This will depend on the size of your home, the number of appliances and devices you use, and your energy consumption habits.
3. The cost and features of different V2H systems
V2H systems vary in price and features. Compare different systems to find one that meets your needs and budget.
Once you have considered these factors, you can start narrowing down your choices and choose the V2H system that is right for you.
4. Some additional tips for choosing a V2H system:
Read reviews. Read reviews of different V2H systems to see what other customers have to say about them.
Get quotes from multiple installers. Get quotes from multiple V2H system installers to compare prices and services.
Make sure the installer is licensed and insured. Make sure the V2H system installer is licensed and insured.
Ask about warranties. Ask about the warranties that are offered on the V2H system and the installation.
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) Technology News and Updates
GM’s Ultium EVs to Become Home Powerhouses by 2026
GM announced that it will expand vehicle-to-home (V2H) bi-directional charging capabilities to all Ultium-based EVs by model year 2026. This means that all future GM EV customers will be able to use their EVs to power their homes and businesses.
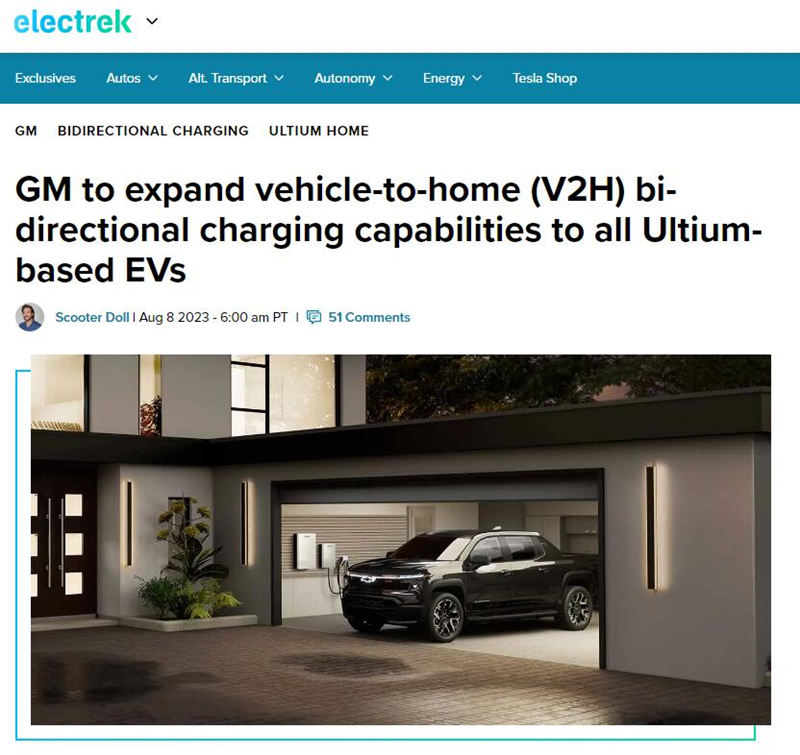
GM Energy, GM’s new energy business unit, is spearheading this expansion. The company has already begun piloting V2H with PG&E in California, and it plans to expand to a subset of residential PG&E customers this year.
GM says that its expanded V2H access will be supported by the rollout of the Ultium Home bundles previously announced. However, the company has not yet released pricing information for this technology.
Panasonic and Omron to enter the Japanese V2H market in 2023
Panasonic and Omron are set to enter the Japanese V2H market in 2023, joining existing players like Nichicon. V2H systems allow electric vehicles (EVs) to be used as home batteries, providing power during blackouts and reducing electricity bills.

Panasonic’s V2H system will be sold through its 5,000 business partners, including electrical contractors and homebuilders. Omron’s V2H system is designed to be lightweight and easy to install by a single worker.
The Japanese V2H market is still in its early stages, but it is expected to grow as EV sales increase and electricity prices soar. Nichicon, which controls around 90% of the Japanese V2H market, is investing 2 billion yen to expand its production capacity.
V2H system makers say that expanding the market will be challenging due to the lack of universal standards for charging and discharging batteries. However, they are committed to working with other stakeholders to develop standards and promote the adoption of V2H technology.
Kia EV9 to Power Your Home and the Electricity Grid
The upcoming Kia EV9 will be the first EV available in Australia with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) charging capability, meaning it can send electricity back to the grid. However, this capability will not be enabled at launch due to regulatory hurdles and the lack of external hardware required to enable V2G in Australia.
Kia says that anyone buying the EV9 will eventually be able to utilise its large battery to send power elsewhere. The hardware for V2G is already standardized on all EV9s, and the company says that all customers will have access to the service when it is ready.
Polestar 3 Bi-directional Charging in Australia
Polestar’s bi-directional charging technology allows the Polestar 3 to send electricity back to the grid, saving money and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
This technology is powered by Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Cockpit Platform and has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about energy, transportation, and sustainability.
Volkswagen and Elli Take Steps to Scale Up V2G/V2H
Volkswagen and Elli, the EV infrastructure and utility arm of automotive OEM Volkswagen, are deploying a second life battery energy storage system (BESS) and launching an electricity trading business. The BESS will be used to test Elli’s digital energy trading platform, which will integrate Volkswagen/Elli’s fleet of EVs via vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) technologies.
The company also plans to deploy more second life BESSs in the future, but the scale it could achieve is not yet clear as the technology is still relatively new. However, Volkswagen is well-positioned in the space as it is involved in the entire lifecycle of a battery.
Renault Introduces Bidirectional Charging with the Renault 5
Renault is introducing bidirectional charging with the Renault 5, its first electric vehicle equipped with a bidirectional charger. This technology allows the car to send electricity back to the grid, which can help to reduce energy costs, increase energy resilience, and support renewable energy.
To use bidirectional charging, customers will need a V2G-capable charging station such as the Mobilize Powerbox. The Mobilize V2G service will also be available, which allows customers to programme bidirectional charging and sell energy back to the grid.
Renault believes that bidirectional charging has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about energy and transportation. It can help to create a more sustainable and affordable energy future.






